Advanced Alert Scheduling in Imply Pivot
Here’s a neat trick when working with Imply Pivot. Imagine you are running an online business, and you want to be notified whenever your online sales fall below a threshold value. You configure an alert to check your sales on an hourly basis but you find a pattern like this:
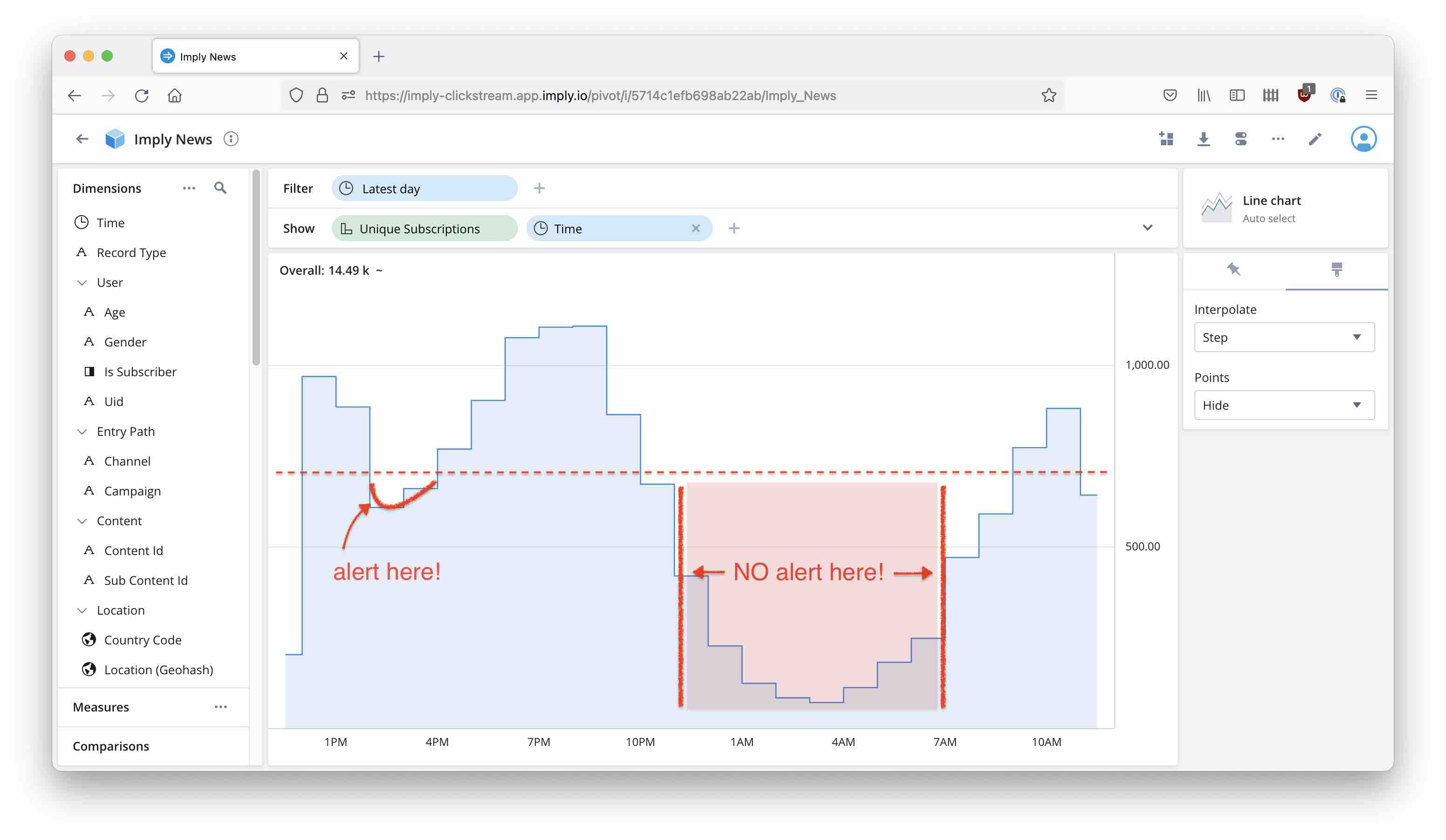
In the small hours of the night, you have low sales but that is expected and you don’t want to have lots of messages during that time. Wouldn’t it be nice to set a more detailed schedule for the alert to be evaluated only during certain hours of the day?
This is possible using multiple alert conditions, and custom measures. Let’s see how!
In this tutorial I am working with Polaris but all steps work the same in Imply Hybrid or Enterprise.
Defining the schedule
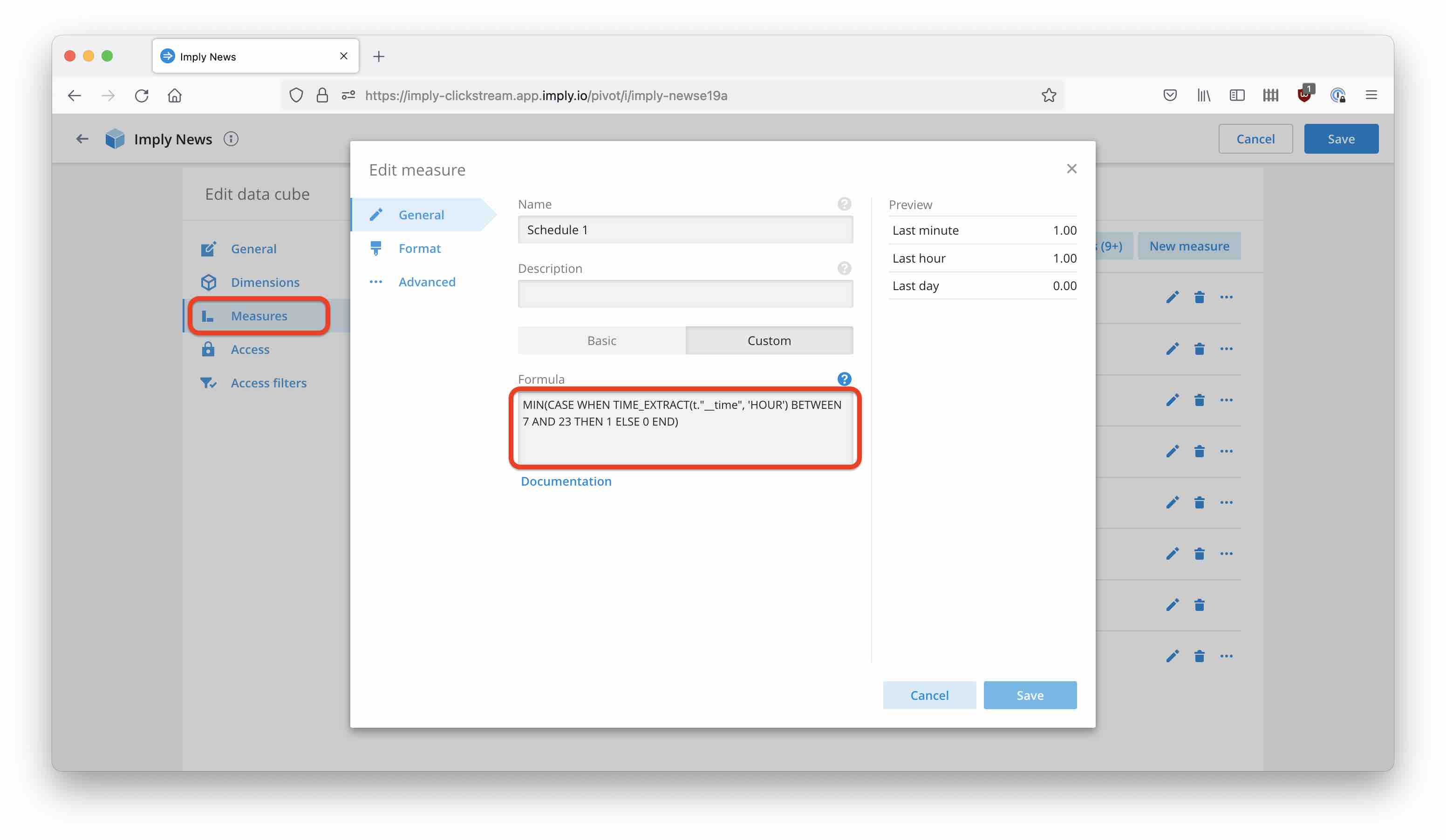
Define the schedule as a custom measure in Pivot. From the cube editor, go to Measures and define a new measure that takes the value 1 when you want the alert to run, and 0 otherwise. I want the alert to fire only between 7am and midnight, so here’s my formula:
MIN(CASE WHEN TIME_EXTRACT(t."__time", 'HOUR') BETWEEN 7 AND 23 THEN 1 ELSE 0 END)
With MIN as the aggregation function, the alert will be masked whenever the aggregation interval overlaps with the quiet zone; you could use MAX to get the opposite behavior.
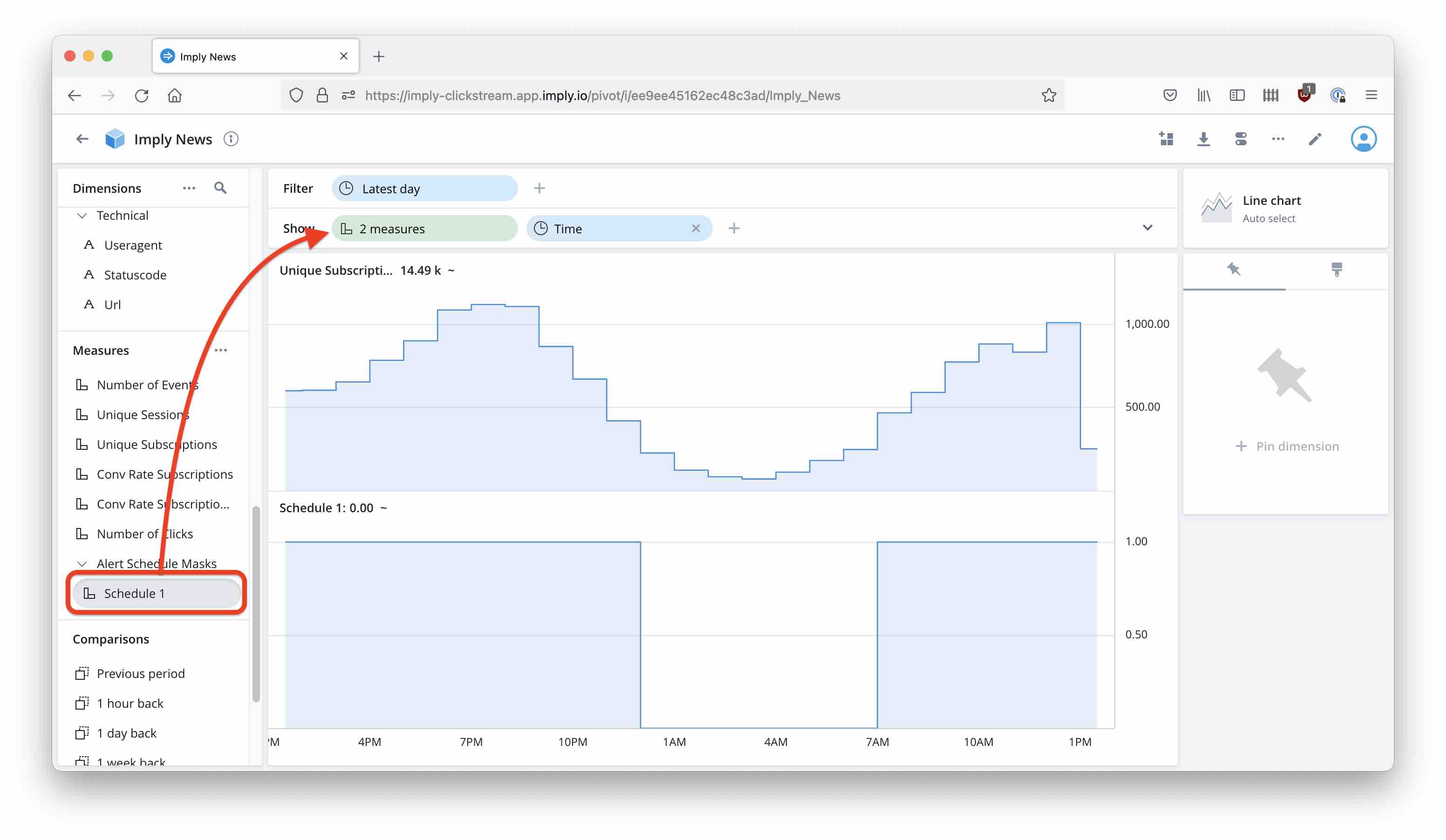
Here you can see how the schedule measure masks the time intervals for which we want to silence the alert:
Defining the alert
Define an alert in Pivot as usual. In my example, the alert is evaluated at the top of the hour and looks back over the last hour:
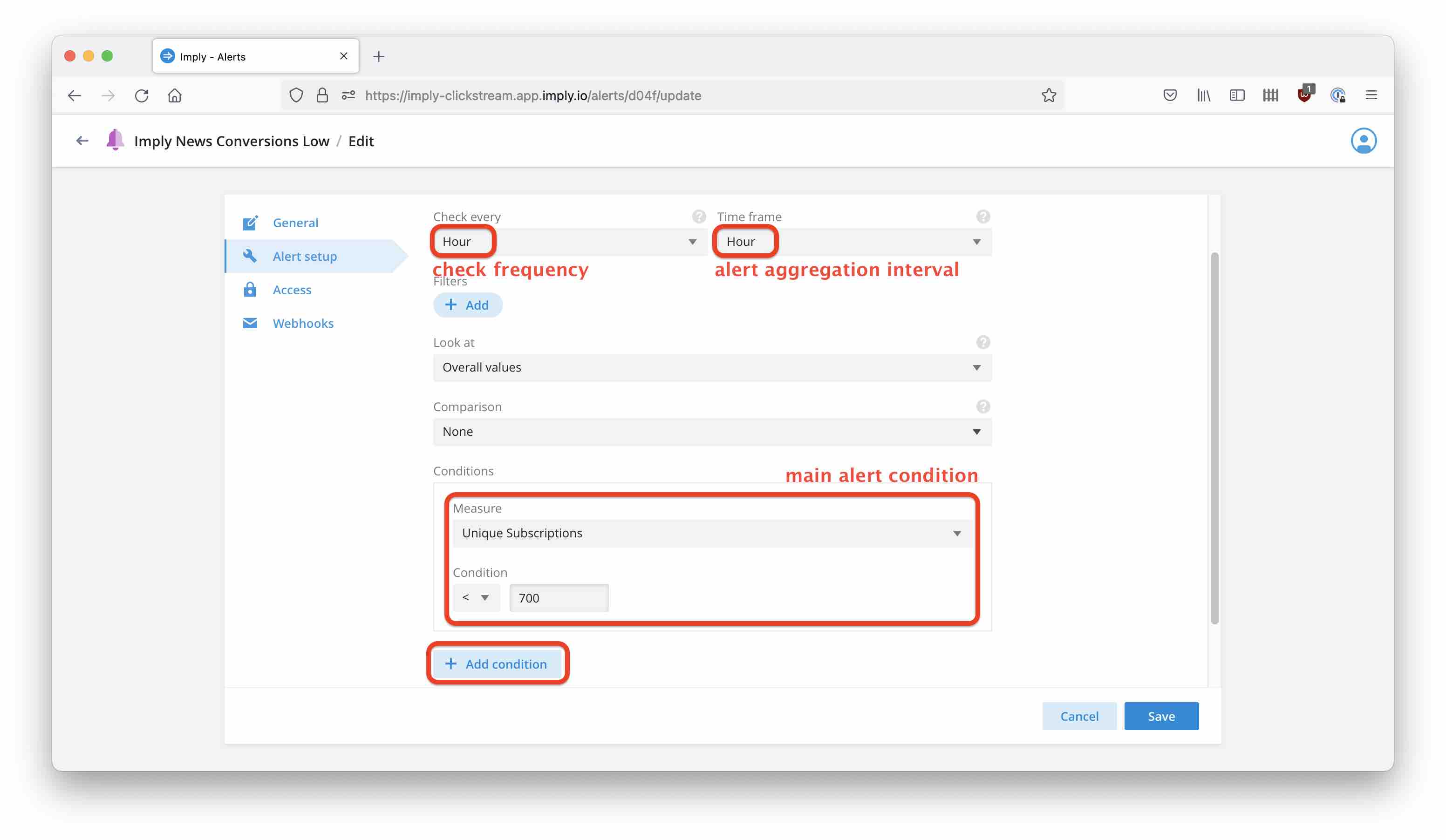
Now, use the Add condition button to add a second alert condition. This is going to be our scheduler mask. Select the measure you defined (here, I called it Schedule 1), and set the condition as > 0.
Make sure to select All conditions on top of the condition definitions.
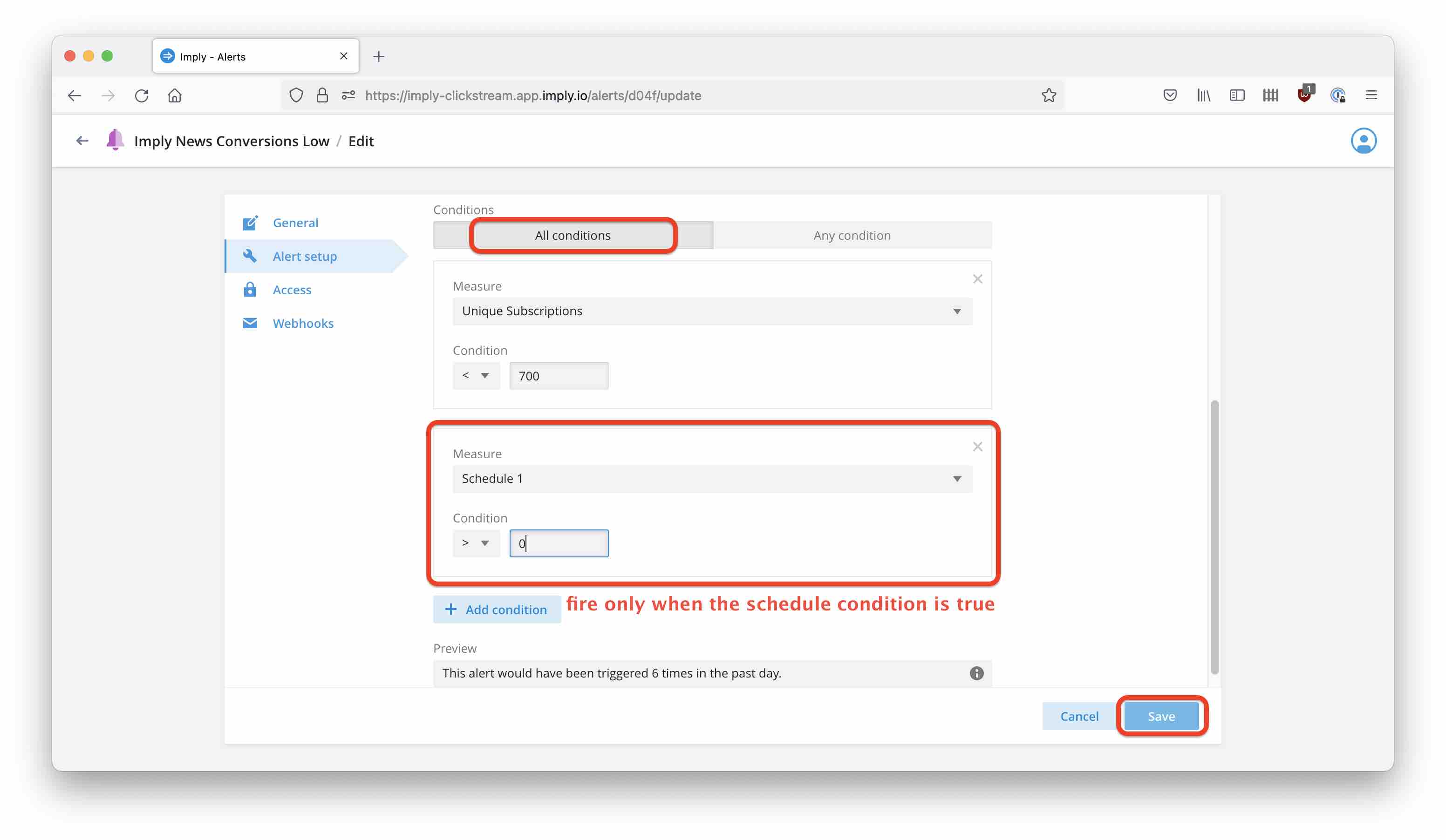
Configure alert delivery according to the documentation.
This can easily be adapted to more complex schedules by using variants of TIME_EXTRACT in the scheduler condition.
Learnings
- Complex scheduler conditions can be implemented in Pivot.
- The way to do this is with measures that are 1 or 0 depending on the scheduler condition.